What May Cause Calcaneal Spur
Overview
A heel spur also known as a calcaneal spur, is a pointed bony outgrowth of the heel bone (calcaneus). Heel spurs do not always cause pain and often are discovered incidentally on X-rays taken for other problems. Heel spurs can occur at the back of the heel and also under the heel bone on the sole of the foot, where they may be associated with the painful foot condition plantar fasciitis.
Causes
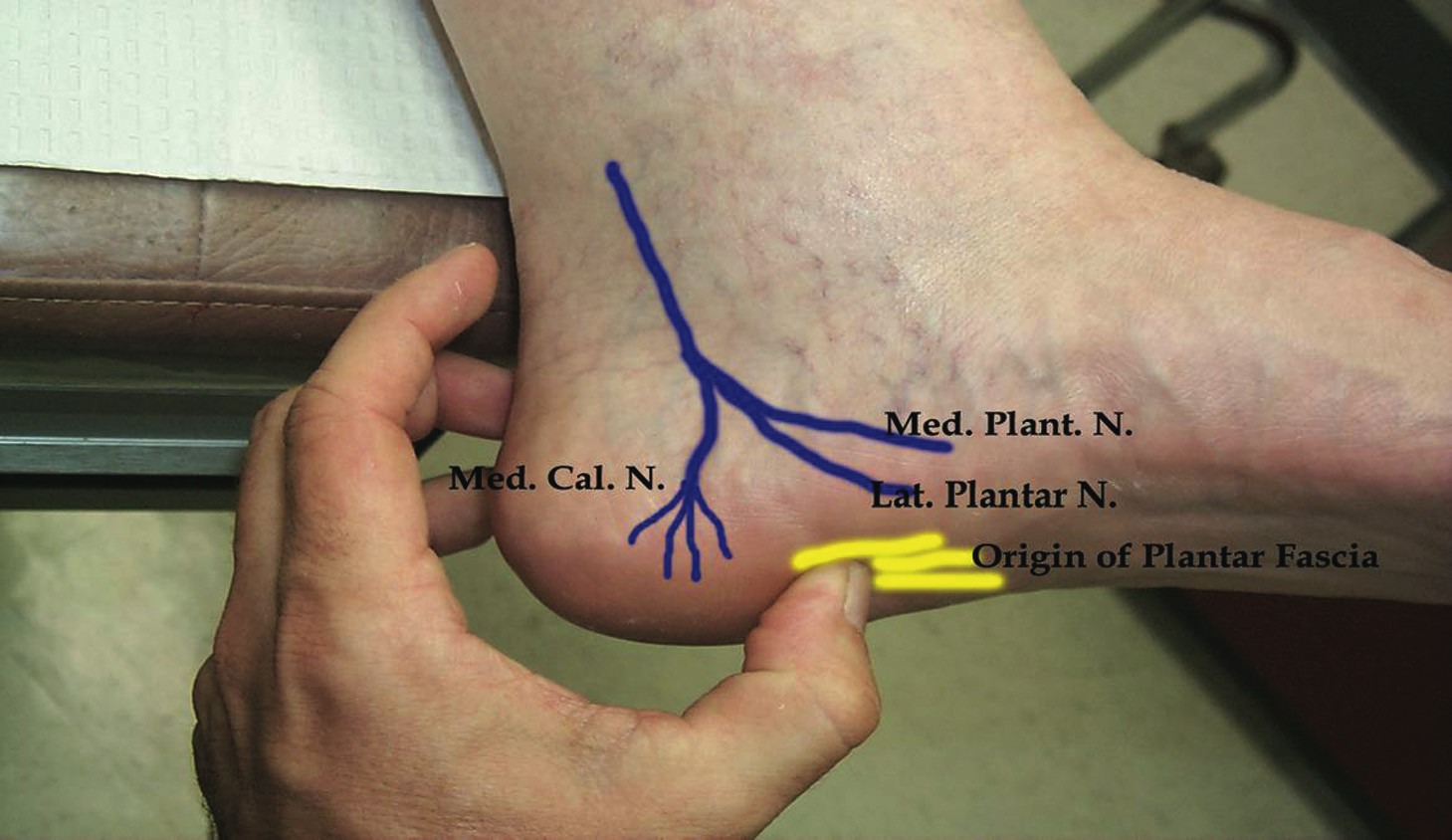
A heel spur is caused by chronic plantar fasciitis. Your plantar fascia is a thick fibrous band of connective tissue originating on the bottom surface of the calcaneus (heel bone) and extending along the sole of the foot towards the toes.Your plantar fascia acts as a passive limitation to the over flattening of you arch. When your plantar fascia develops micro tears or becomes inflamed it is known as plantar fasciitis. When plantar fasciitis healing is delayed or injury persists, your body repairs the weak and injured soft tissue with bone. Usually your injured fascia will be healed via fibroblastic activity. They'll operate for at least six weeks. If your injury persists beyond this time, osteoblasts are recruited to the area. Osteoblasts form bone and the end result is bone (or calcification) within the plantar fascia or at the calcaneal insertion. These bone formations are known as heel spurs. This scenario is most common in the traction type injury. The additional bone growth is known as a heel spur or calcaneal spur.

Symptoms
It is important to be aware that heel spurs may or may not cause symptoms. Symptoms are usually related to the plantar fasciitis. You may experience significant pain and it may be worse in the morning when you first wake up or during certain physical activities such as, walking, jogging, or running.
Diagnosis
A thorough medical history and physical exam by a physician is always necessary for the proper diagnosis of heel spurs and other foot conditions. X rays of the heel area are helpful, as excess bone production will be visible.
Non Surgical Treatment
Over-the-counter or prescription-strength anti-inflammatory medications can help temporarily, but can cause side effects with prolonged use - the most significant being gastrointestinal upset, ulceration and bleeding. Deep tissue massage, taping and other physical therapy modalities can also be helpful. Arch support is highly recommended, either with shoe inserts or custom orthotics made by podiatrists. If pain continues, a steroid injection at the site of pain may be recommended; however, many physicians do not like injecting around the heel. The side effects of steroids injected in this area can be serious and worsen symptoms. Complications can include fat necrosis (death of fatty tissue) of the heel and rupture of the plantar fascia.
Surgical Treatment
Sometimes bone spurs can be surgically removed or an operation to loosen the fascia, called a plantar fascia release can be performed. This surgery is about 80 percent effective in the small group of individuals who do not have relief with conservative treatment, but symptoms may return if preventative measures (wearing proper footwear, shoe inserts, stretching, etc) are not maintained.
Prevention
If you have not yet developed this condition, you can take steps to protect yourself from it. Most importantly, make it a rule to wear properly fitted footwear. Avoid shoes that have become worn down in the heel, and don't choose shoes that cause you to walk in an abnormal fashion. Maintaining a healthy weight will ensure that undue pressure isn't being put on the ligaments, tendons and bones of your feet. If your job requires a great deal of time on your feet, or if you exercise regularly, be sure to balance periods of activity with periods of rest for your feet.