Bursitis Foot Pain Symptoms
Bursitis accounts for 0.4% of all visits to primary care clinics. The most common locations of bursitis are the subdeltoid, olecranon, ischial, trochanteric, and prepatellar bursae. The incidence of bursitis is higher in athletes, reaching levels as high as 10% in runners. Approximately 85% of cases of septic superficial bursitis occur in men. A French study aimed at assessing the prevalence of knee bursitis in the working population found that most cases occurred in male workers whose occupations involved heavy workloads and frequent kneeling. Mortality in patients with bursitis is very low. The prognosis is good, with the vast majority of patients receiving outpatient follow-up and treatment.
Causes
Normally, only one bursa is in the heel, between the Achilles tendon and the heel bone (calcaneus). This bursa may become inflamed, swollen, and painful, resulting in anterior Achilles tendon bursitis. Abnormal pressure and foot dysfunction can cause a protective bursa to form between the Achilles tendon and the skin. This bursa may also become inflamed, swollen, and painful, resulting in posterior Achilles tendon bursitis.
Symptoms
Pain at the back of the heel at the attachment site of the Achilles tendon when running. Pain on palpation of the back of the heel or bottom of heel. Pain when standing on tiptoes. Swelling and redness at the back and bottom of the heel.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will take a history to find out if you have the symptoms of retrocalcaneal bursitis. By examining your ankle, he or she can generally tell the location of the pain. The physician will look for tenderness and redness in the back of the heel. The pain may be worse when the doctor bends the ankle upward (dorsiflex), as this may tighten the achilles tendon over the inflamed bursa. Alternatively, the pain may be worse with toe rise, as this puts stress on the attachment of the achilles tendon to the heel bone. Imaging studies such as X-ray and MRI are not usually necessary at first. If initial treatment fails to improve the symptoms, these studies may be obtained. MRI may show inflammation.
Non Surgical Treatment
The most important factor in healing bursitis is resting your foot and ankle. This can be difficult when you have to carry on with daily activities, but resting and elevating your foot whenever you can is recommended. During your recovery you will probably have to modify or avoid the activities that stress your bursa until your pain and inflammation settle.
Surgical Treatment
Only if non-surgical attempts at treatment fail, will it make sense to consider surgery. Surgery for retrocalcanel bursitis can include many different procedures. Some of these include removal of the bursa, removing any excess bone at the back of the heel (calcaneal exostectomy), and occasionally detachment and re-attachment of the Achilles tendon. If the foot structure and shape of the heel bone is a primary cause of the bursitis, surgery to re-align the heel bone (calcaneal osteotomy) may be considered. Regardless of which exact surgery is planned, the goal is always to decrease pain and correct the deformity. The idea is to get you back to the activities that you really enjoy. Your foot and ankle surgeon will determine the exact surgical procedure that is most likely to correct the problem in your case. But if you have to have surgery, you can work together to develop a plan that will help assure success.
Prevention
You can avoid the situation all together if you stop activity as soon as you see, and feel, the signs. Many runners attempt to push through pain, but ignoring symptoms only leads to more problems. It?s better to take some time off right away than to end up taking far more time off later. Runners aren?t the only ones at risk. The condition can happen to any type of athlete of any age. For all you women out there who love to wear high-heels-you?re at a greater risk as well. Plus, anyone whose shoes are too tight can end up with calcaneal bursitis, so make sure your footwear fits. If the outside of your heel and ankle hurts, calcaneal bursitis could be to blame. Get it checked out.
Flexible Hammertoe Treatment
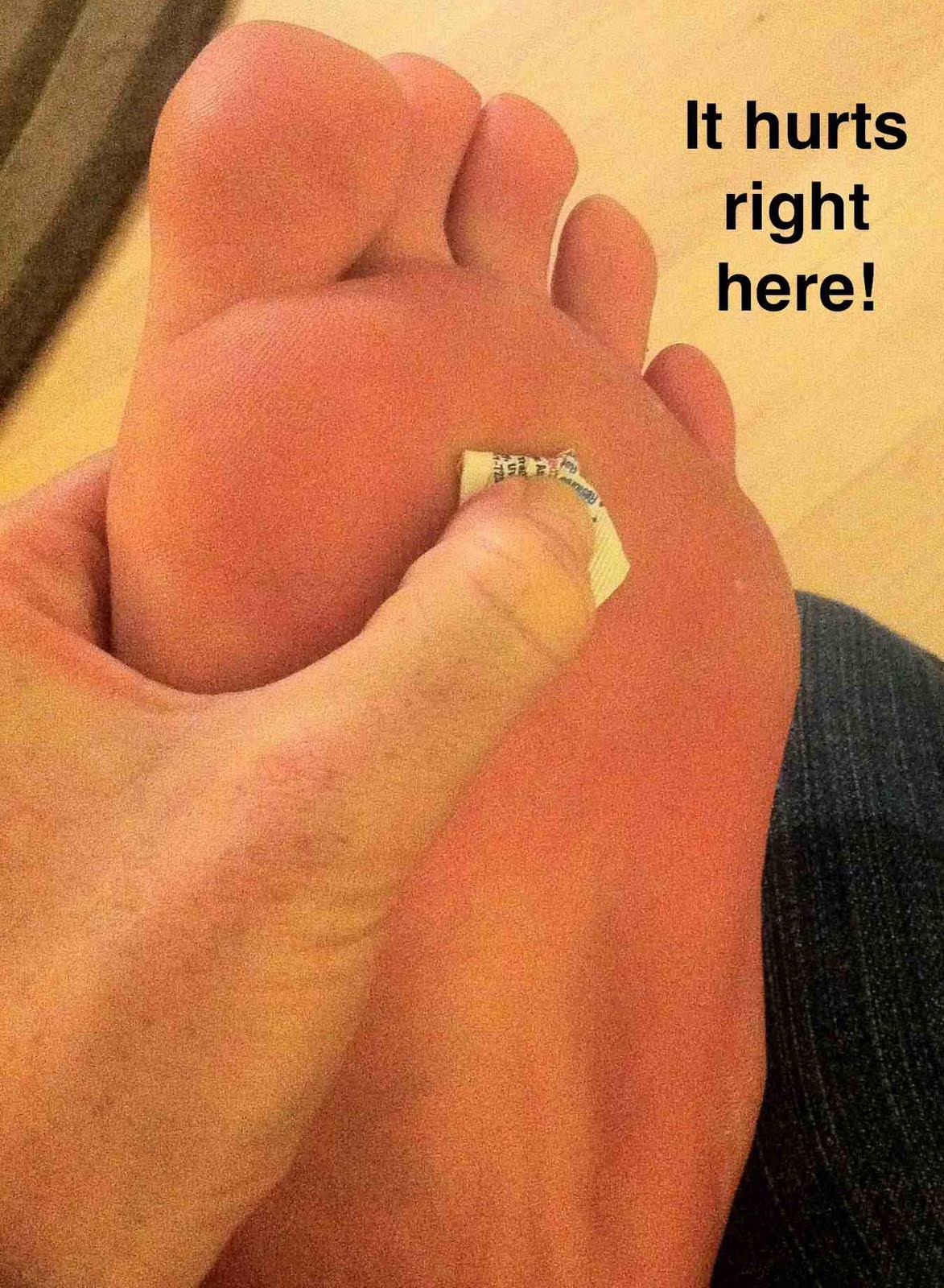 Overview
Overview
The smallest four toes of each foot have three bony segments connected by two joints, just as the fingers do. hammertoe is a deformity in which one or more of the small toes develops a bend at the joint between the first and second segments so that the tip of the toe turns downward, making it looks like a hammer or claw. The second toe is affected most often.
Causes
Hammer toe most frequently results from wearing poorly fitting shoes that can force the toe into a bent position, such as excessively high heels or shoes that are too short or narrow for the foot. Having the toes bent for long periods of time can cause the muscles in them to shorten, resulting in the hammer toe deformity. This is often found in conjunction with bunions or other foot problem (e.g., a bunion can force the big toe to turn inward and push the other toes). It can also be caused by muscle, nerve, or joint damage resulting from conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, stroke, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, complex regional pain syndrome or diabetes. Hammer toe can also be found in Friedreich's ataxia.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
Hammer toe is often distinguished by a toe stuck in an upside-down ?V? position, and common symptoms include corns on the top of your toe joint. Pain at the top of a bent toe when you put on your shoes. Pain when moving a toe joint. Pain on the ball of your foot under the bent toe. Corns developing on the top of the toe joint. It is advisable to seek medical advice if your feet hurt on a regular basis. It is imperative to act fast and seek the care of a podiatrist or foot surgeon. By acting quickly, you can prevent your problem from getting worse.
Diagnosis
The earlier a hammertoe is diagnosed, the better the prognosis and treatment hammertoe options. Your doctor will be able to diagnose your hammertoe with a simple examination of the foot and your footwear. He or she may take an x-ray to check the severity of the condition. You may also be asked about your symptoms, your normal daily activities, and your medical and family history.
Non Surgical Treatment
Conservative treatment starts with new shoes that have soft, roomy toe boxes. Shoes should be one-half inch longer than your longest toe. For many people, the second toe is longer than the big toe.) Avoid wearing tight, narrow, high-heeled shoes. You may also be able to find a shoe with a deep toe box that accommodates the hammer toe. Or, a shoe repair shop may be able to stretch the toe box so that it bulges out around the toe. Sandals may help, as long as they do not pinch or rub other areas of the foot.
Surgical Treatment
Hammer toe can be corrected by surgery if conservative measures fail. Usually, surgery is done on an outpatient basis with a local anesthetic. The actual procedure will depend on the type and extent of the deformity. After the surgery, there may be some stiffness, swelling and redness and the toe may be slightly longer or shorter than before. You will be able to walk, but should not plan any long hikes while the toe heals, and should keep your foot elevated as much as possible.
Could Hammertoes Cause Numbness
A Hammer toe is a deformity of the second, third or fourth toe in which the toe becomes bent at the middle joint; hence, it resembles a hammer. Claw toe and mallet toe are related conditions. While a hammer toe is contracted at the first toe joint, a mallet toe is contracted at the second toe joint, and a claw toe is contracted at both joints. According to the 2012 National Foot Health Assessment conducted by the NPD Group for the Institute for Preventive Foot Health, 3 percent of U.S. adults age 21 and older (about 7 million people) have experienced hammer toe or claw toe. The condition is significantly more prevalent in females than in males.
Causes
Hammertoe is caused when muscles fail to work in a balanced manner and the toe joints bend to form the hammertoe shape. If they remain in this position, the muscles and tendons supporting them tighten and stay that way. Causes of hammertoe can include squeezing into a too-small or ill-fitting shoe or wearing high heels that jam your toes into a tight toe box. An injury such as badly stubbing your toe. Arthritis. Nerve and muscle damage from diseases such as diabetes,
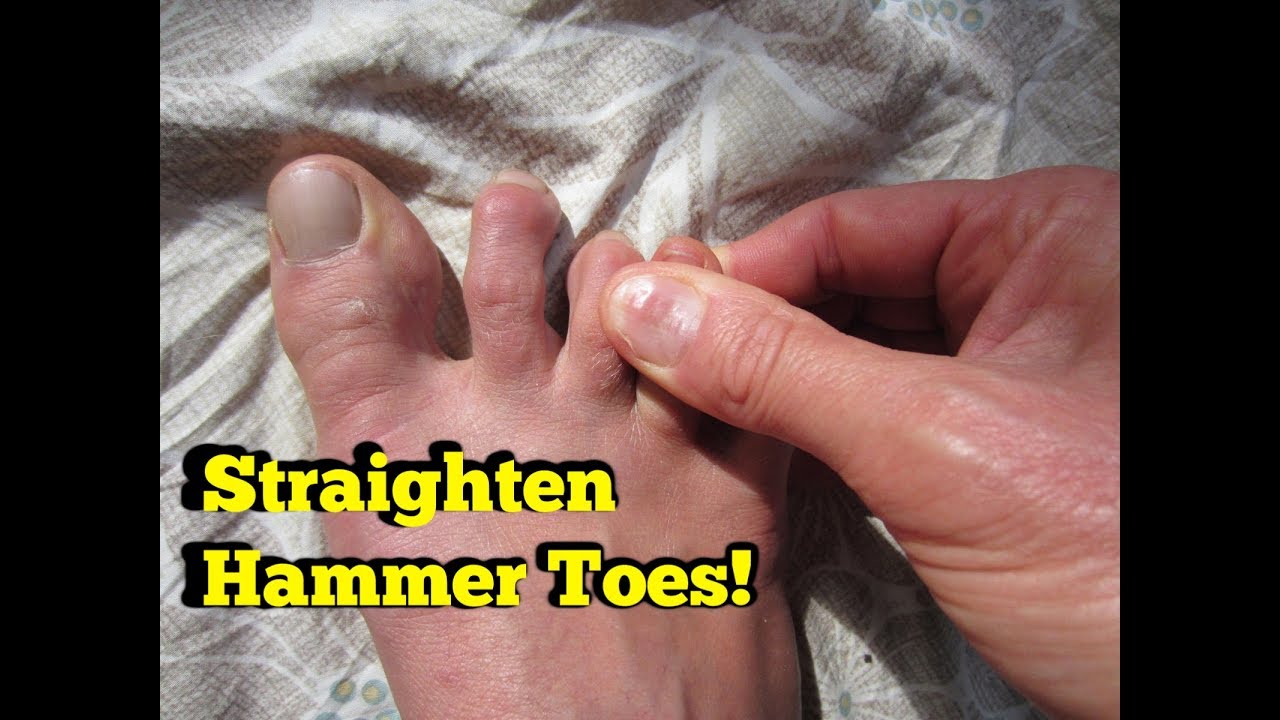 Symptoms
Symptoms
A hammer toe may be painful, especially when irritated by a shoe. All four toe conditions may cause cramps in the toes, foot and leg due to the abnormal function of the tendons in the foot. If a mallet toe has occurred, you are likely to suffer from a corn at the end of the toe. A hammertoe may cause a corn on the top of the toe. Infections and ulcers can also occur. In severe cases a mallet toe, trigger toe, claw toe or a hammer toe may create a downward pressure on the foot, which can result in hard skin and corns on the soles of the feet.
Diagnosis
Your healthcare provider will examine your foot, checking for redness, swelling, corns, and calluses. Your provider will also measure the flexibility of your toes and test how much feeling you have in your toes. You may have blood tests to check for arthritis, diabetes, and infection.
Non Surgical Treatment
Conservative treatment is limited to accommodation, not correction, of the deformity, though some patients find the relief they can get from these options to be more than Hammer toes enough to put off or even avoid surgery. These include better Footwear. Shoe gear with a wider toe box and higher volume causes less friction to the toes. Toe Braces and Strapping. Some toe braces and strapping techniques take some pressure off the toes during gait. Custom molded orthotics can redistribute the forces through the tendons that control the toe, lessening the pain and extent of the deformity.The calluses on the toe and the ball of the foot can be shaved occasionally to reduce some pain and pressure, although they will return due to the constant deformity.
Surgical Treatment
As previously mentioned it?s best to catch this problem early; hammer toe taping is relatively harmless and simple. Long term complications can cause foot deformities and even difficulty walking. It?s always best to stiff shoes and high heel, especially if you?re working on hammer toe recovery. Pick comfortable shoes with plenty of toe space. Prevention is the best cure here as this injury is nearly always self inflicted.
 Prevention
Prevention
Be good to your feet, because they carry you. They are designed to last a lifetime, but that doesn?t mean they don?t need some love and care as well as some basic maintenance. Check your feet regularly for problems. This is especially true if you have diabetes or any other medical condition that causes poor circulation or numbness in your toes. If you do, check your feet every day so problems can be caught early on. Good circulation is essential. When you're sitting down, put your feet up. If you've been sitting for a while, stretch your legs and feet. Give yourself a foot massage, or ask someone you love for a foot massage. A warm foot bath is also a good idea.
Do Bunions Involve Surgery
Overview
 Even though bunions are a common foot condition, they are probably the one with the most misconceptions. Many people suffer unnecessarily with the pain of bunions for years before seeking treatment out of fear about the ?surgery?. The good news is that most bunion pain can be resolved without surgery.
Even though bunions are a common foot condition, they are probably the one with the most misconceptions. Many people suffer unnecessarily with the pain of bunions for years before seeking treatment out of fear about the ?surgery?. The good news is that most bunion pain can be resolved without surgery.
Causes
The main cause of bunions is a mechanical imbalance in the feet which is usually inherited. The mechanical imbalance is known as overpronation, where the feet roll in towards the arch and big toe. This added weight and stress transfer towards the big toe, causes instability in the structures of this area and a bunion develops.
Symptoms
Your bunion may not cause any symptoms. Or you may have pain in your big toe, red or irritated skin over the bunion, and swelling at the base of the big toe. The big toe may point toward the other toes and cause problems in other toes, such as hammer toe . A bunionette can cause similar symptoms at the base of the little toe.
Diagnosis
Most patients are diagnosed to have bunions from clinical history and examination. However, in some cases, X-rays will be performed to determine the extent of damage to the joint. Furthermore, it will enable the treating doctor to decide on the best course of management of the patient.
Non Surgical Treatment
Conservative Treatment. Apply a commercial, nonmedicated bunion pad around the bony prominence. Wear shoes with a wide and deep toe box. If your bunion becomes inflamed and painful, apply ice packs several times a day to reduce swelling. Avoid high-heeled shoes over two inches tall. See your podiatric physician if pain persists. Orthotics. Shoe inserts may be useful in controlling foot function and may reduce symptoms and prevent worsening of the deformity. Padding & Taping. Often the first step in a treatment plan, padding the bunion minimizes pain and allows the patient to continue a normal, active life. Taping helps keep the foot in a normal position, thus reducing stress and pain. Medication. Anti-inflammatory drugs and cortisone injections are often prescribed to ease the acute pain and inflammations caused by joint deformities. Physical Therapy. Often used to provide relief of the inflammation and from bunion pain. Ultrasound therapy is a popular technique for treating bunions and their associated soft tissue involvement. 
Surgical Treatment
According to the NHS, 85 per cent of operations are successful, but there?s no guarantee that the problem won?t recur, that the pain will go away, or that your movement won?t become limited. Ask yourself if the affront to your vanity and discomfort caused by your bunion is worth the post-op suffering, and if you can cope with the inevitable restriction on your movement that means no driving and time off work, even if only for a few weeks.
What Actually Will Cause Feet To Over Pronate
Overpronation and underpronation describe general foot movements. These terms do not necessarily describe a medical problem with a foot. For example, you can overpronate and not have any problems or symptoms at all. It is important to have your foot structure and symptoms adequately assessed by your prescribing physician and a qualified practitioner. Once the underlying conditions and mechanical faults are assessed, an appropriate treatment plan including possible orthotic and footwear recommendations can be made.

Causes
Overpronation often occurs in people with flat feet, whose plantar fascia ligament is too flexible or too long, and therefore unable to properly support the longitudinal arch of the foot. People tend to inherit the foot structure that leads to overpronation. In a normal foot the bones are arranged so that two arches are formed, the longitudinal and the transverse. Ligaments hold all the bones in their correct positions, and tendons attach muscles to bones. If the bones are held together too loosely, they will tend to move inwards as this is the easiest direction for them to go. Over time the soft tissue structures will adjust to the misalignment and the foot will become permanently over-flexible, with a flat arch.
Symptoms
When standing, your heels lean inward. When standing, one or both of your knee caps turn inward. Conditions such as a flat feet or bunions may occur. You develop knee pain when you are active or involved in athletics. The knee pain slowly goes away when you rest. You abnormally wear out the soles and heels of your shoes very quickly.
Diagnosis
When sitting, an over-pronating foot appears quite normal, i.e. showing a normal arch with room under the underside of the foot. The moment you get up and put weight on your feet the situation changes: the arches lower and the ankle slightly turns inwards. When you walk or run more weight is placed on the feet compared to standing and over-pronation will become more evident. When walking barefoot on tiles or timber floors over-pronation is more visible, compared to walking on carpet or grass.

Non Surgical Treatment
Not all over pronation is treated. Although, when it appears to be a causitive factor that is contributing to pain,or development of structural deformities, there are various degrees of treatment.In some cases specific shoes may be all that is required. In other cases, paddings or strapping, are prescribed and where necessary orthotic therapy. A podiatric assesment would be advised to asses this.
Prevention
Custom-made orthotics supports not only the arch as a whole, but also each individual bone and joint that forms the arch. It is not enough to use an over-the-counter arch support, as these generic devices will not provide the proper support to each specific structure of the arch and foot. Each pronated foot?s arch collapses differently and to different degrees. The only way to provide the support that you may need is with a custom-made device. This action of the custom-made orthotic will help to prevent heel spurs, plantar fasciitis, calluses, arch pain, and weakness of the entire foot.
What Is Calcaneal Apophysitis?
Sever's disease occurs in children when the growth plate (which is the growing part of the heel) is injured. The foot is one of the first body parts to grow to full size. This usually occurs in early puberty. During this time, bones often grow faster than muscles and tendons. As a result, muscles and tendons become tight. The heel area is less flexible. During weight-bearing activity (activity performed while standing), the tight heel tendons may put too much pressure at the back of the heel (where the Achilles tendon attaches). This can injure the heel and cause Sever's disease.
Causes
Sever?s disease is often an overuse injury. It can be caused by playing sports, especially those involving high impact. Sever?s disease can also be linked to growth which can place a stress on the attachment of the Achilles tendon.
Symptoms
A few signs and symptoms point to Sever?s disease, which may affect one or both heels. These include Pain at the heel or around the Achilles tendon, Heel pain during physical exercise, especially activities that require running or jumping, Worsening of pain after exercise, A tender swelling or bulge on the heel that is sore to touch, Calf muscle stiffness first thing in the morning, Limping, A tendency to tiptoe.
Diagnosis
Sever condition is diagnosed by detecting the characteristic symptoms and signs above in the older children, particularly boys between 8 and 15 years of age. Sometimes X-ray testing can be helpful as it can occasionally demonstrate irregularity of the calcaneus bone at the point where the Achilles tendon attaches.
Non Surgical Treatment
The surgeon may select one or more of the following options to treat calcaneal apophysitis. Reduce activity. The child needs to reduce or stop any activity that causes pain. Support the heel. Temporary shoe inserts or custom orthotic devices may provide support for the heel. Medications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, help reduce the pain and inflammation. Physical therapy. Stretching or physical therapy modalities are sometimes used to promote healing of the inflamed issue. Immobilization. In some severe cases of pediatric heel pain, a cast may be used to promote healing while keeping the foot and ankle totally immobile. Often heel pain in children returns after it has been treated because the heel bone is still growing. Recurrence of heel pain may be a sign of calcaneal apophysitis, or it may indicate a different problem. If your child has a repeat bout of heel pain, be sure to make an appointment with your foot and ankle surgeon.
Surgical Treatment
The surgeon may select one or more of the following options to treat calcaneal apophysitis. Reduce activity. The child needs to reduce or stop any activity that causes pain. Support the heel. Temporary shoe inserts or custom orthotic devices may provide support for the heel. Medications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, help reduce the pain and inflammation. Physical therapy. Stretching or physical therapy modalities are sometimes used to promote healing of the inflamed issue. Immobilization. In some severe cases of pediatric heel pain, a cast may be used to promote healing while keeping the foot and ankle totally immobile. Often heel pain in children returns after it has been treated because the heel bone is still growing. Recurrence of heel pain may be a sign of calcaneal apophysitis, or it may indicate a different problem. If your child has a repeat bout of heel pain, be sure to make an appointment with your foot and ankle surgeon.
Correcting Flat Feet In Adults
Overview
The posterior tibial tendon serves as one of the major supporting structures of the foot, helping it to function while walking. Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD) is a condition caused by changes in the tendon, impairing its ability to support the arch. This results in flattening of the foot. PTTD is often called ?adult acquired flatfoot? because it is the most common type of flatfoot developed during adulthood. Although this condition typically occurs in only one foot, some people may develop it in both feet. PTTD is usually progressive, which means it will keep getting worse, especially if it isn?t treated early. 
Causes
Rheumatoid arthritis This type of arthritis attacks the cartilage in the foot, leading to pain and flat feet. It is caused by auto-immune disease, where the body?s immune system attacks its own tissues. Diabetes. Having diabetes can cause nerve damage and affect the feeling in your feet and cause arch collapse. Bones can also fracture but some patients may not feel any pain due to the nerve damage. Obesity and/or hypertension (high blood pressure) This increases your risk of tendon damage and resulting flat foot.
Symptoms
The symptom most often associated with AAF is PTTD, but it is important to see this only as a single step along a broader continuum. The most important function of the PT tendon is to work in synergy with the peroneus longus to stabilize the midtarsal joint (MTJ). When the PT muscle contracts and acts concentrically, it inverts the foot, thereby raising the medial arch. When stretched under tension, acting eccentrically, its function can be seen as a pronation retarder. The integrity of the PT tendon and muscle is crucial to the proper function of the foot, but it is far from the lone actor in maintaining the arch. There is a vital codependence on a host of other muscles and ligaments that when disrupted leads to an almost predictable loss in foot architecture and subsequent pathology.
Diagnosis
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction is diagnosed with careful clinical observation of the patient?s gait (walking), range of motion testing for the foot and ankle joints, and diagnostic imaging. People with flatfoot deformity walk with the heel angled outward, also called over-pronation. Although it is normal for the arch to impact the ground for shock absorption, people with PTTD have an arch that fully collapses to the ground and does not reform an arch during the entire gait period. After evaluating the ambulation pattern, the foot and ankle range of motion should be tested. Usually the affected foot will have decreased motion to the ankle joint and the hindfoot. Muscle strength may also be weaker as well. An easy test to perform for PTTD is the single heel raise where the patient is asked to raise up on the ball of his or her effected foot. A normal foot type can lift up on the toes without pain and the heel will invert slightly once the person has fully raised the heel up during the test. In early phases of PTTD the patient may be able to lift up the heel but the heel will not invert. An elongated or torn posterior tibial tendon, which is a mid to late finding of PTTD, will prohibit the patient from fully rising up on the heel and will cause intense pain to the arch. Finally diagnostic imaging, although used alone cannot diagnose PTTD, can provide additional information for an accurate diagnosis of flatfoot deformity. Xrays of the foot can show the practitioner important angular relationships of the hindfoot and forefoot which help diagnose flatfoot deformity. Most of the time, an MRI is not needed to diagnose PTTD but is a tool that should be considered in advanced cases of flatfoot deformity. If a partial tear of the posterior tibial tendon is of concern, then an MRI can show the anatomic location of the tear and the extensiveness of the injury.
Non surgical Treatment
The adult acquired flatfoot is best treated early. Accurate assessment by your doctor will determine which treatment is suitable for you. Reduce your level of activity and follow the RICE regime. R - rest as often as you are able. Refrain from activity that will worsen your condition, such as sports and walking. I - ice, apply to the affected area, ensure you protect the area from frostbite by applying a towel over the foot before using the ice pack. C - compression, a Tubigrip or elasticated support bandage may be applied to relieve symptoms and ease pain and discomfort. E - elevate the affected foot to reduce painful swelling. You will be prescribed pain relief in the form of non-steroidal antiinflammatory medications (if you do not suffer with allergies or are asthmatic). Immobilisation of your affected foot - this will involve you having a below the knee cast for four to eight weeks. In certain circumstances it is possible for you to have a removable boot instead of a cast. A member of the foot and ankle team will advise as to whether this option is suitable for you. Footwear is important - it is advisable to wear flat sturdy lace-up shoes, for example, trainers or boots. This will not only support your foot, but will also accommodate orthoses (shoe inserts). 
Surgical Treatment
For patients with a more severe deformity, or significant symptoms that do not respond to conservative treatment, surgery may be necessary. There are several procedures available depending on the nature of your condition. Ligament and muscle lengthening, removal of inflamed tendon lining, transferring of a nearby tendon to re-establish an arch, and bone realignment and fusion are examples of surgical options to help with a painful flatfoot condition. Surgery can be avoided when symptoms are addressed early. If you are feeling ankle pain or notice any warmth, redness or swelling in your foot, contact us immediately. We can create a tailored treatment plan to resolve your symptoms and prevent future problems.